Recently, the global spread of the monkeypox outbreak has attracted widespread attention, with many drawing comparisons to the COVID-19 pandemic. This article will explore the similarities and differences between the monkeypox virus (MPXV) and the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) to help the public better understand these two viruses and take appropriate preventive measures.
The monkeypox virus and the novel coronavirus are two distinctly different pathogens that have garnered varying levels of public health attention worldwide. Although both have been declared Public Health Emergencies of International Concern (PHEIC) by the World Health Organization (WHO), they exhibit significant differences in terms of virus type, modes of transmission, symptoms, and case fatality rates.
Virus Type: The monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus of the Poxviridae family and is a DNA virus, while the novel coronavirus is a coronavirus that belongs to the RNA virus category. DNA viruses are generally more stable than RNA viruses, which means the monkeypox virus may mutate at a slower rate than the novel coronavirus.
Mode of Transmission: The monkeypox virus is primarily spread through close contact, especially skin-to-skin contact, including contact with the pustules of an infected person or contact with objects contaminated with the virus. In contrast, the novel coronavirus can spread through respiratory droplets and aerosols, which allows for more rapid and widespread transmission among people.
Symptoms: Symptoms of monkeypox include fever, body aches, rash, and characteristic pustules, which are similar to those of smallpox. The monkeypox rash goes through stages from macules, papules, vesicles to pustules, and finally crusts. The symptoms of COVID-19 include fever, dry cough, and fatigue, with severe cases potentially experiencing difficulty breathing.
Case Fatality Rate: The case fatality rate for monkeypox is generally low, while the case fatality rate for COVID-19 varies by region and time but is typically lower than that of other coronavirus diseases such as SARS and MERS. The case fatality rate for monkeypox also differs among various strains, with the West African strain having a fatality rate of about 1%, while the Congo Basin strain can have a fatality rate as high as 10%.
Vaccine Effectiveness: Several monkeypox virus mRNA vaccines have entered clinical trial stages. Due to the similarity between the monkeypox virus and the smallpox virus, the smallpox vaccine also offers some protection against monkeypox, which is why it is currently used for prevention. Vaccines for the novel coronavirus, on the other hand, are specifically developed to target SARS-CoV-2.
Response Measures: For the monkeypox virus, given its relatively lower transmission rate and harm, the main preventive measures currently include maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and vaccination when necessary. For the novel coronavirus, due to its high transmissibility, in addition to personal protective measures, broader public health measures are also required, such as social distancing, wearing masks, and mass vaccination campaigns.
Although monkeypox and COVID-19 are both global public health challenges, their modes of transmission, symptoms, and response strategies differ. Understanding these differences is crucial for devising effective prevention measures and public health policies. The public should remain vigilant and follow the guidance of health authorities to reduce the risk of transmission for both viruses.

Additionally, the detection methods for monkeypox and COVID-19 each have their own characteristics, suitable for different testing needs and stages.
Detection methods for monkeypox virus: The laboratory detection of monkeypox virus mainly includes nucleic acid testing and virus culture. Nucleic acid testing detects the monkeypox virus's nucleic acid in specimens such as rashes, pustules, scabs, oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal secretions using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. This method is the "gold standard" for monkeypox testing, known for its high sensitivity and specificity. Virus culture is performed in biosafety level 3 or higher laboratories, where the monkeypox virus can be isolated from the aforementioned specimens, but this method requires a longer time and higher biosafety requirements. In addition, monkeypox testing also includes antibody detection, but it is mainly used for research purposes and is not widely used for clinical diagnosis. Polymerase chain reaction testing is currently the only recommended method for monkeypox detection, while rapid testing methods are not yet widely utilized.
Detection methods for the novel coronavirus: The detection methods for the novel coronavirus include nucleic acid testing, antibody testing, and antigen testing. Nucleic acid testing is the "gold standard" for COVID-19 detection, which uses RT-PCR technology to detect the virus's RNA, characterized by early diagnosis, high sensitivity, and specificity. Antibody testing detects the presence and levels of specific antibodies IgM and IgG through blood samples, and can serve as a supplementary means to nucleic acid diagnosis. However, due to the limitations of "false positives" and "false negatives," it is not suitable for screening the general population. Antigen testing detects the virus's proteins, but its detection rate is relatively low, and it is not currently a primary detection method. Nucleic acid testing usually takes 2-3 hours, while the colloidal gold method in antibody testing can yield results in a short time (about 15 minutes), but it requires time for serum sample processing. Chemiluminescent immunoassay takes 30-60 minutes, offers high sensitivity and specificity, but has higher requirements for equipment and operation.
In summary, both monkeypox and COVID-19 detection methods include nucleic acid testing, but monkeypox testing also includes virus culture, while COVID-19 testing also includes antibody and antigen testing. Different detection methods are suitable for different situations and purposes, and choosing the appropriate testing method is crucial for controlling the epidemic and diagnosing patients.
GDSBIO, as a leading enterprise in the field of biotechnology, plays a significant role in molecular diagnostics with its developed fluorescent quantitative detection reagents. These reagents, known for their high sensitivity and specificity, provide a reliable detection foundation for monkeypox and COVID-19 nucleic acid testing kits. By employing real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology, the reagent can effectively amplify the genetic material of the virus to a detectable level, enabling precise identification and quantitative analysis of the monkeypox virus and the novel coronavirus. This product from GDSBIO not only enhances the accuracy of testing but also significantly reduces the detection time, offering strong technical support for epidemic prevention and patient management.
Recommended Products:
① Product Name: Multiplex Probe qPCR Mix Plus U
Catalog Numbers: P2701/P2702/P2703/P2704
Human genomic DNA (0.1ng/µl) is used as a template for gene detection with the Multiplex Probe qPCR Mix Plus U. Figures 1 and 2 show the amplification curves obtained from detection immediately after the reaction system is prepared (0 hr) and after being placed at room temperature (25℃) for 48 hours (48 hr), respectively; simultaneously, a comparative test is conducted with the similar product from Manufacturer T, with Figures 3 and 4 showing the amplification curves of Manufacturer T's product at 0 hr and 48 hr after assembly, respectively. Table 2 presents the Ct values of Multiplex Probe qPCR Mix Plus U and Manufacturer T's product at 0 hr and 48 hr. It can be observed that even after being placed at room temperature for 48 hours, the Multiplex Probe qPCR Mix Plus U still exhibits excellent amplification performance.
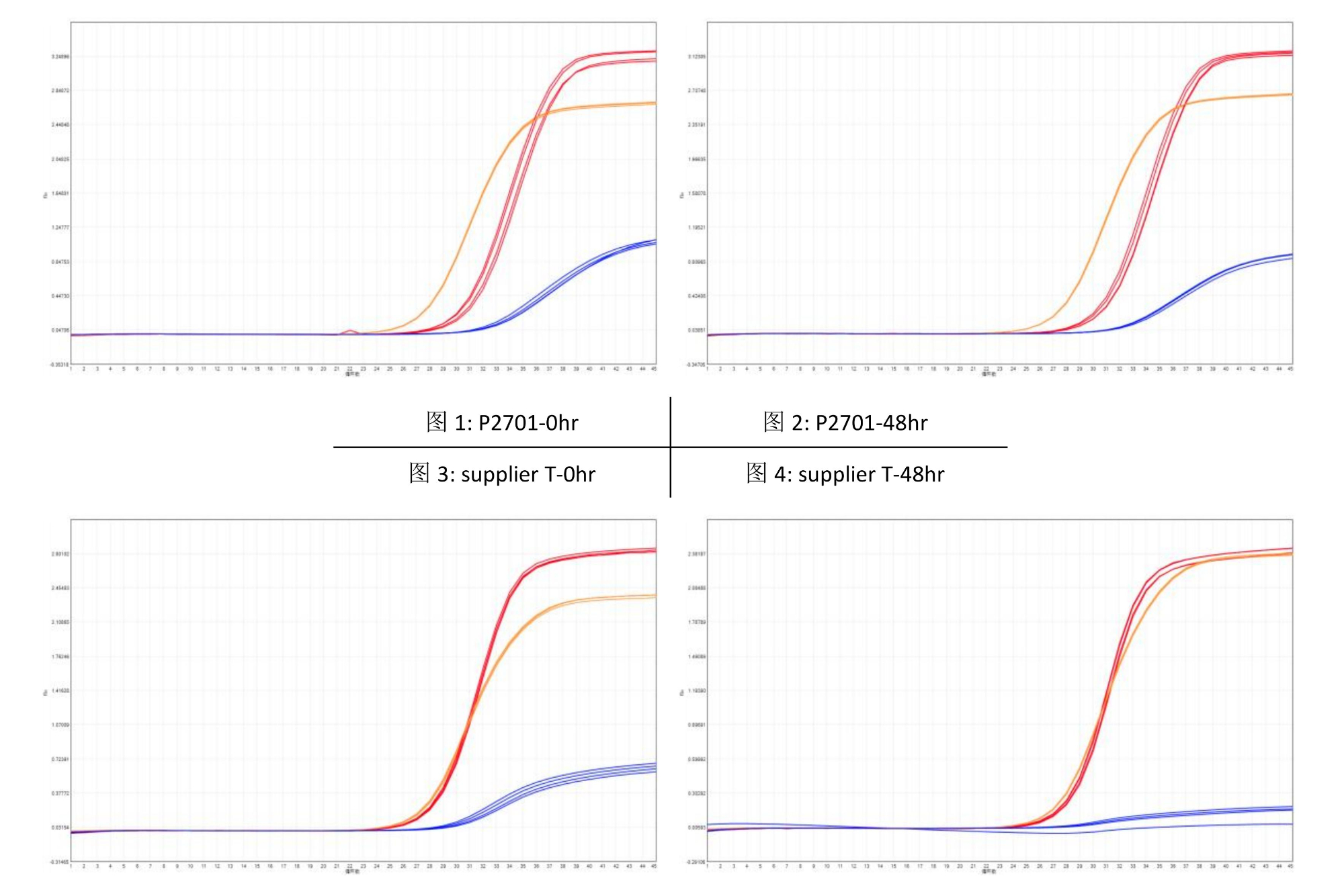
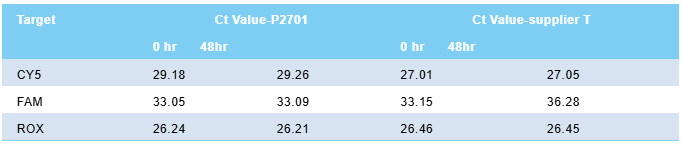
table 2. ct value
② Product Name: DSPath 4X One-Step Multiplex Master Mix
Catalog Numbers: V5005/V5006
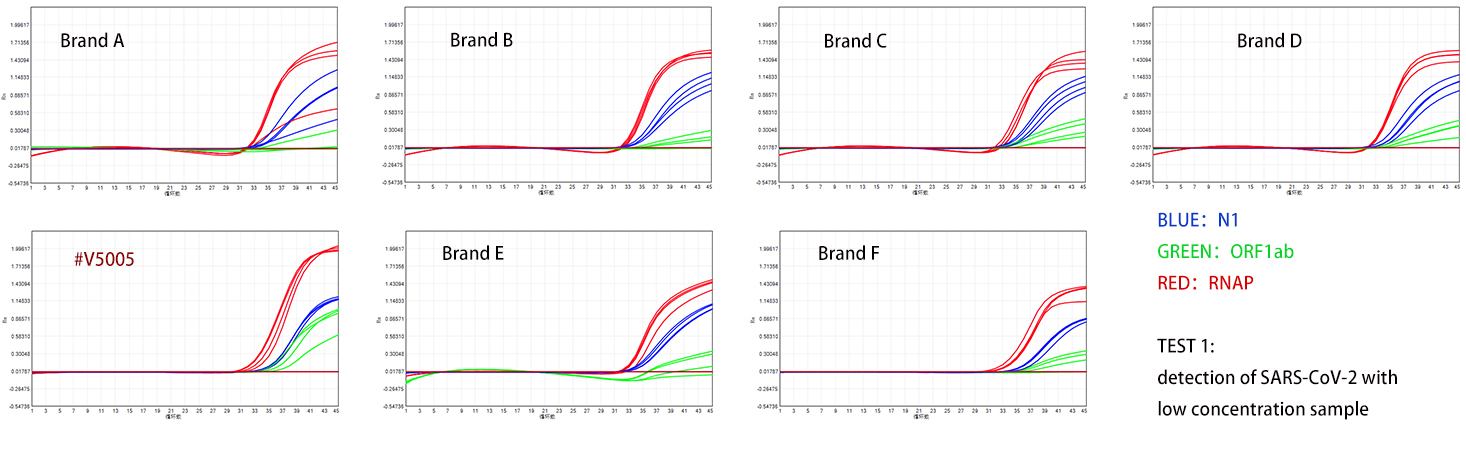
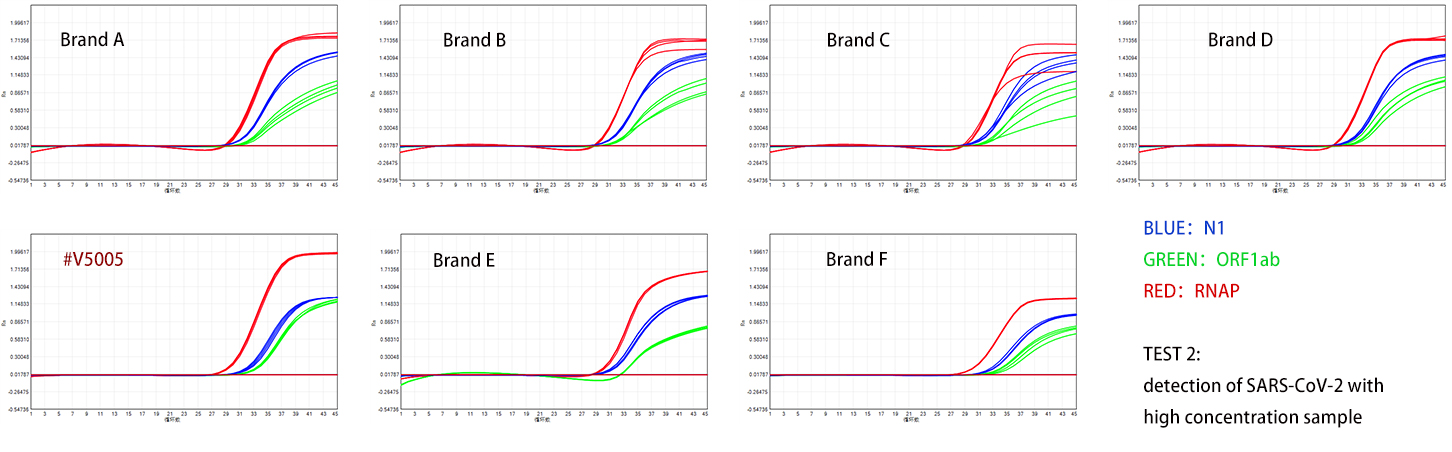
The product is used to detect two groups of COVID-19 pseudovirus RNA with different concentrations, with the high concentration group being ten times that of the low concentration group. According to the test results shown in Figures 1 and 2, the specificity and sensitivity of the Dongsheng V5005 detection are superior to those of four domestic manufacturers, and its performance is also excellent when compared with two internationally renowned brands.
Additionally, by detecting the four target sequences of SARS-CoV-2, an 8-day stability test was conducted on DSPath 4X One-Step Multiplex Master Mix/MixB/MixC/MixD (with different ion concentrations) at a condition of 37°C. As shown in Figures 3 and 4, the amplification efficiency of these four products did not change significantly, indicating that they all maintain high stability and are easy to transport and store for long periods.
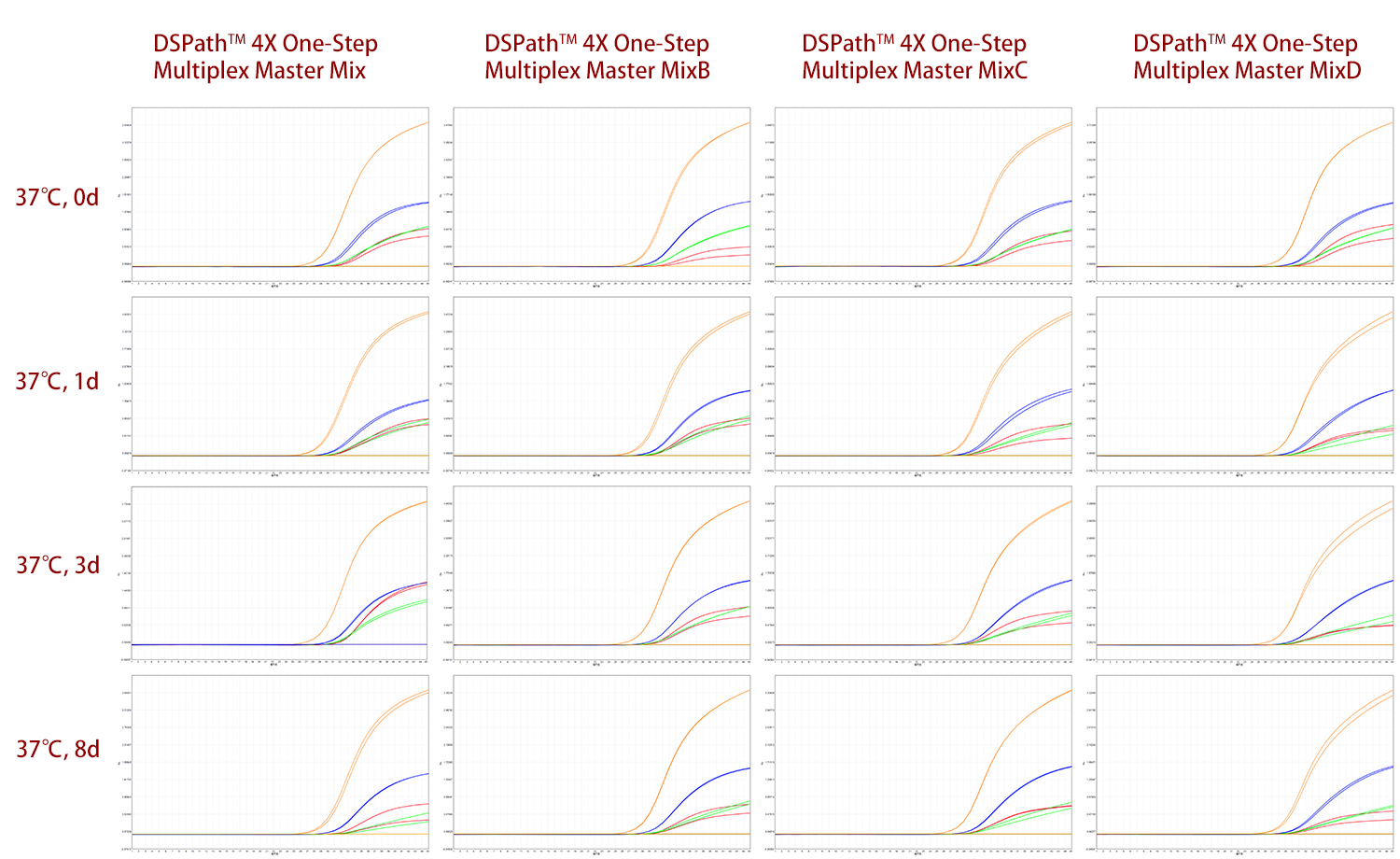
fig 3. amplifiaction curve of DSPath 4X One-Step Multiplex Master Mix/MixB/MixC/MixD
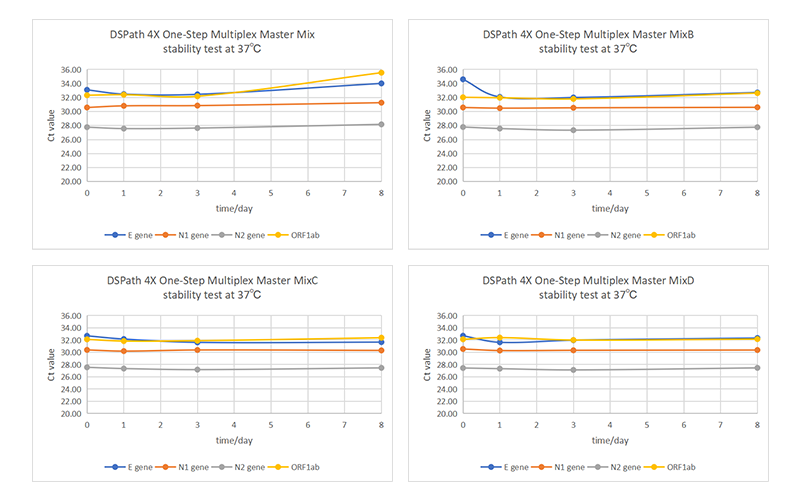
fig 4. Ct Value Trend of DSPath 4X One-Step Multiplex Master Mix/MixB/MixC/MixD
③ Product Name: One-step Probe RT-qPCR Kit V3
Catalog Numbers: V5011/V5011-2
The kit is used for quadruplex probe detection of RNA viruses, providing accurate results without interference.

Using COVID-19 pseudovirus RNA as a template, the kit detects the E gene target sequence, two N gene target sequences, and the ORF1ab sequence of the novel coronavirus with high amplification efficiency and good repeatability.








 Tel: +86 20 31600213
Tel: +86 20 31600213  Sales EMail: order@gdsbio.com
Sales EMail: order@gdsbio.com 






